[ad_1]
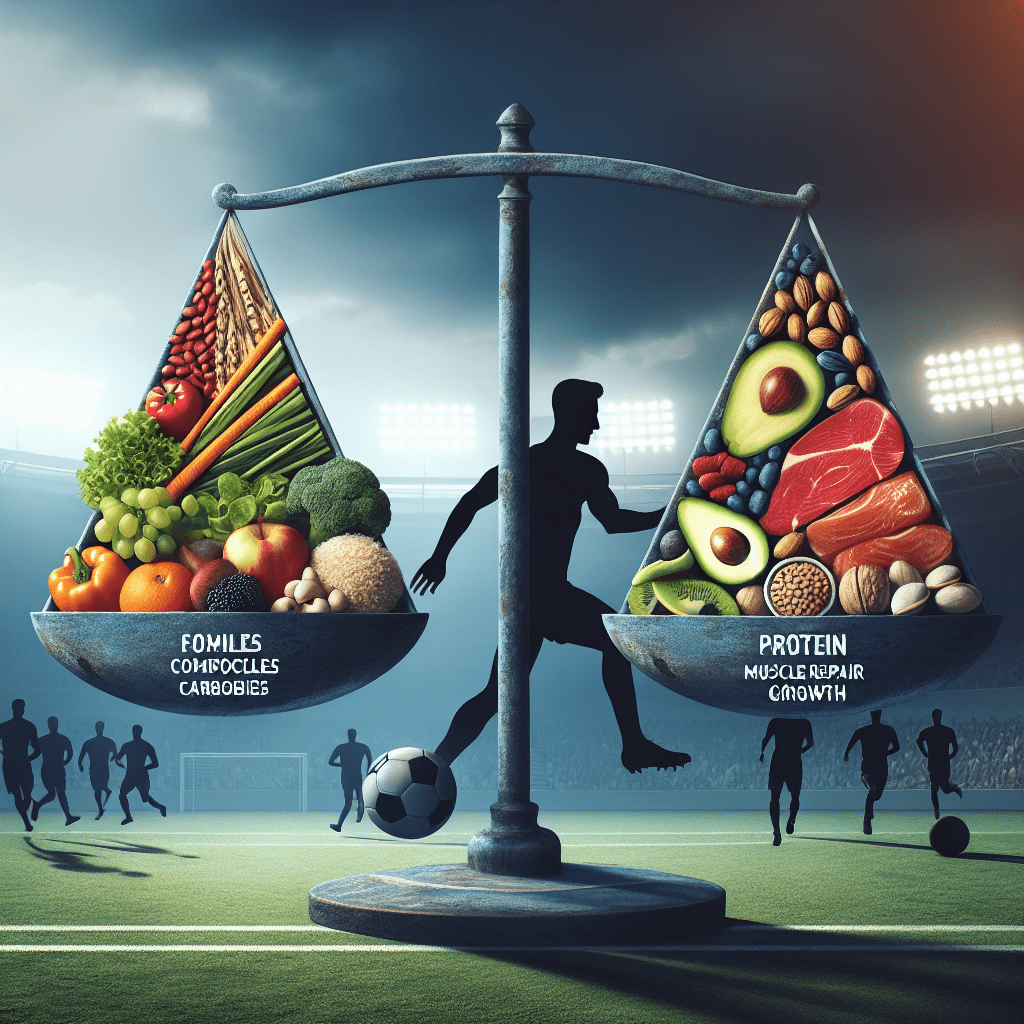
Success in soccer not only requires talent and practice but also a well-planned nutrition strategy. Balancing the right amount of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats – the three primary macronutrients – is essential for maximum performance and recovery. In this article, we dive deep into how soccer players can optimize their nutrition by understanding and implementing the best balance of these macronutrients.
Carbohydrates: The Energy Powerhouse
Carbohydrates are the primary fuel source for high-intensity sports like soccer. They are stored in the muscles and liver as glycogen, which is readily available energy during short bursts of activity or throughout a prolonged match. The right amount of carbs helps maintain optimal energy levels, delay fatigue, and improve overall performance.
- Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes are excellent sources of carbohydrates.
- Recommended intake: 55-65% of your total daily calories.
Proteins: Building and Repairing Muscles
Protein is critical for muscle repair, growth, and maintenance, especially for athletes. After intense training or matches, muscles are often damaged and require protein to heal and grow stronger. Incorporating a sufficient amount of protein in your diet can help speed up recovery times and enhance muscular adaptations to training.
- Lean meats, fish, dairy, eggs, and plant-based proteins like beans and lentils are great sources.
- Recommended intake: 15-20% of your total daily calories or 1.2-1.7 grams per kg of body weight.
Fats: Essential, But Moderately
While often vilified, fats are crucial for long-term energy storage, nutrient absorption, and hormone production. They become a significant energy source during prolonged physical activities when glycogen stores are low. However, it’s important to focus on healthy fats.
- Avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil are sources of good fats.
- Recommended intake: 20-30% of your total daily calories, with a focus on unsaturated fats and limiting saturated fat intake.
Hydration: The Unsung Hero
While not a macronutrient, proper hydration is vital for peak performance. Water regulates body temperature, lubricates joints, and helps transport nutrients to give you energy and keep you healthy. Soccer players should aim to stay hydrated before, during, and after games and practices.
Implementing Your Macronutrient Balance
Understanding your individual needs is crucial as they can vary greatly depending on your age, gender, weight, height, and level of activity. Consulting with a sports nutritionist can provide personalized advice tailored to your goals.
Key Takeaways
- Carbohydrates should be your main source of energy as a soccer player.
- Protein is crucial for muscle repair and growth.
- Healthy fats are essential but should be consumed in moderation.
- Hydration is key to optimal performance and recovery.
- Personalized nutrition plans can provide the best results.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many carbs should a soccer player eat?
A soccer player should aim to get 55-65% of their daily calories from carbohydrates. The exact number can vary based on the player’s specific energy demands.
Is protein important for soccer players?
Yes, protein is vital for soccer players for muscle repair, growth, and overall recovery. Aim for 15-20% of your daily calories from protein or 1.2-1.7 grams per kg of body weight.
Can fats be part of a soccer player’s diet?
Definitely. Fats are essential for long-term energy, nutrient absorption, and hormone production. Focus on healthy fats and keep them to 20-30% of your daily caloric intake.
How can I balance these macronutrients in my diet?
Start by focusing on food quality and variety within each macronutrient group. Consider consulting a sports nutritionist for personalized advice based on your individual needs and goals.
[ad_2]